This is how fish will prolong your life!!, benefits and properties of fish

Fish? In ancient times we had a diet that included bushmeat, wild fruit, and fish. All those foods contained adequate doses of Omega-3 oil.
Today, fish is the only widely available source of "wild" foods. The reason for the high values of Omega-3 is that it affects functions such as blood clotting and inflammation and causes a series of processes ranging from immune responses to the development of the eye-brain binomial.
Although we now mostly believe that cholesterol is to blame for heart disease, researchers are beginning to think that it is only a secondary factor.
We already know other factors that contribute to these problems: lack of exercise, obesity, excess fat in the diet, hypertension, tobacco, alcohol, and drugs.

For example, high blood pressure, coupled with cholesterol, can damage artery walls.
In an attempt to repair it, cell material and cholesterol join forces to close off the inside of the artery.
This combined substance, called plaque, narrows the passage and decreases blood flow, leading to heart disease.
Damaged areas also stimulate blood clots, opening the way for a heart attack.
BENEFITS OF FISH
- It's a natural anticoagulant.
- Also, it helps lower cholesterol levels.
- It helps prevent cancer.
- Fish is very high in Omega-3 acids.
- It helps us lose weight.
- Also, it is a cardiac protector.
- It helps to lower triglycerides.
- Fish has just a few calories.
- It helps to strengthen the bones because of its high calcium content.
- Fish is a high protein food.
- It is effortless to digest, which is why doctors recommend it in the diets of patients.
- It has a high content of vitamins and minerals.
NUTRITIONAL VALUE OF THE MOST COMMON FISH
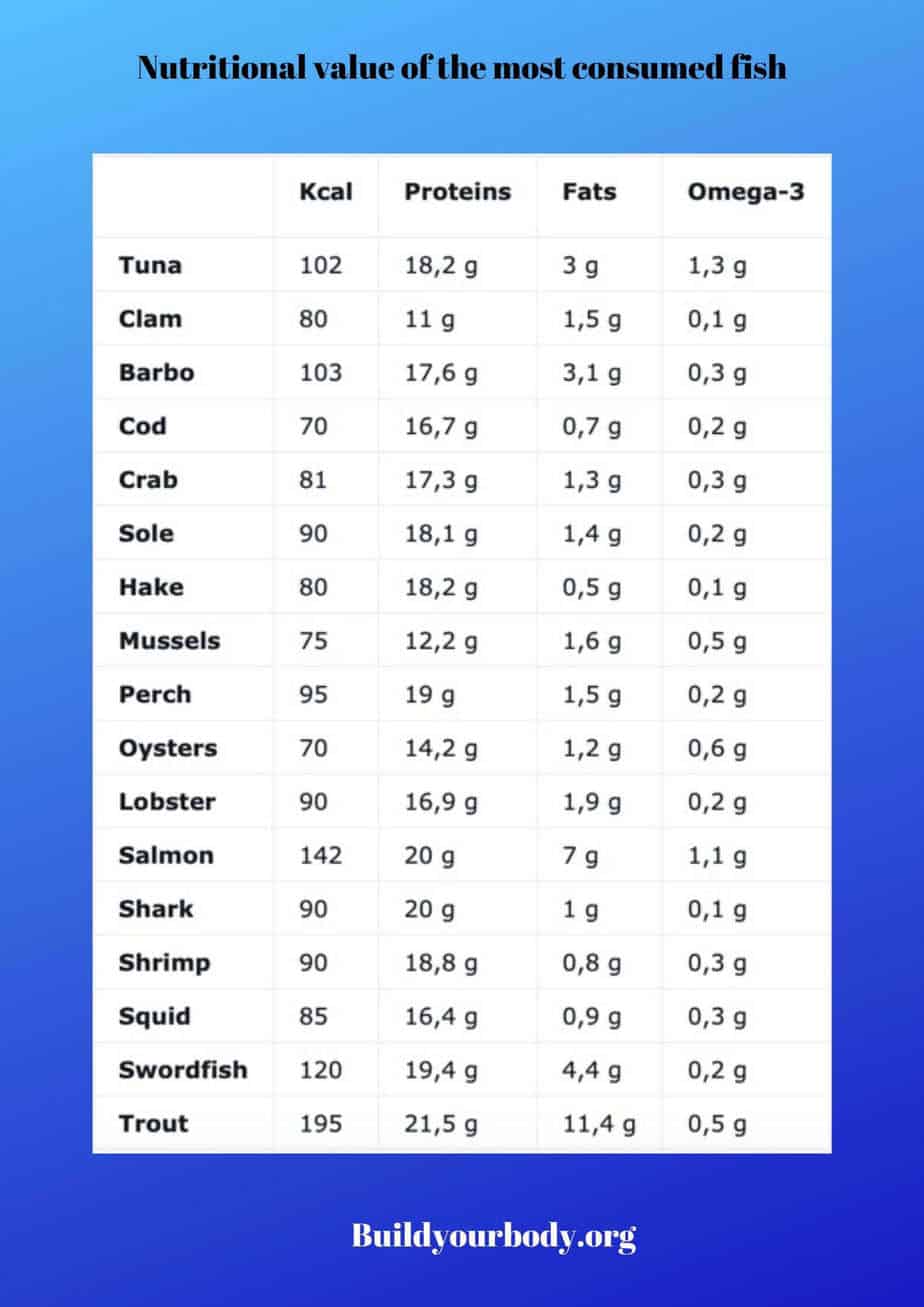
As you can see, we have not included carbohydrates because the amounts contained in them are residual.
OMEGA-3 AND HEART DISEASE
Omega-3 acids inhibit blood clots and, in fact, broaden the diameter of the arteries, increasing blood flow.
Two decades ago, they revealed that very few Eskimos died of heart attack despite their diets high in cholesterol and fat.
However, half of all Western deaths at that time were due to cardiovascular failure.
Current studies support the idea that fish protects the heart. Japanese fishers suffer less from heart disease than Japanese farmers, who eat less fish.
A Dutch study has shown that people who take fish a couple of times a week have a heart death rate lower than half of those who don't take it.

It is a great food to take care of your heart
The result was that the diet high in fish and fish oil produced the most significant drop in cholesterol and triglyceride, despite their high fat and cholesterol content.
Each person in the study had a decrease in cholesterol and triglycerides. Half of them - with fluid problems - had a 45 percent drop in their total cholesterol and a 79 percent drop in triglycerides.
However, a regular diet of two or three fish per week produces satisfactory results without the risk of overdose.
Fish oils make the bloodless dense, which reduces the pain and discomfort inherent in a heart attack by increasing blood flow to the heart, providing the essential oxygen.
Preventing heart disease is not the only role of fish oil. Omega-3 also affects immunity and inflammation. Coupled with regular medication, it relieves the symptoms of arthritis gives very significant form.
SHOULD I INCLUDE FISH IN MY DIET?

With the introduction of agriculture some 10,000 years ago, the base of our foods were seeds and grains, which are very rich in oils such as Omega-3.
It could be a positive change, but was it? Scientists believe that natural, unprocessed foods, such as those containing Omega-3 and Omega-6, produce a nutritional benefit.
But with agriculture and the latest technology, we have been able to extract oil from miles and grains. People move away from animal fats and return to unsaturated vegetable oils, destroying the natural balance between the two types of fatty acids.
The tissues surrounding joints afflicted with arthritic rheumatism contain large amounts of an Omega-6-derived substance commonly found in vegetable oils.
Some studies suggest that Omega-3 may be useful in controlling specific chronic skin problems such as eczema and psoriasis. Its use for psoriasis is auspicious.
Dermatologist Vincent Zboth found that treating psoriasis patients with large amounts of low-fat diets and Omega-6s reduced their ailments.
If you want more information on diets and food, visit our nutrition section.
OMEGA-3 AND CANCER

Fish appears to be excellent for preventing certain types of cancer. Animals that followed a diet rich in Omega-3 suffered fewer tumors than those that took a lot of Omega-6. Fish oil proved to have a possible benefit in fighting colon and prostate cancers.
Fish oil appears to increase T-cell response, a key component of immunity, while corn oil does not. Omega-6 fatty acids produce a substance that can suppress the immune system's ability to destroy tumor cells. Unfortunately, studies have only used laboratory animals, not people.
The cancer protection hypothesis stems from the fact that Japanese and Eskimos have low rates of breast cancer, and both take a lot of fish.
Therefore, the research goes so far as to suggest that our bodies may need Omega-3 to function correctly.
One type of Omega-3, DHA, appears in large concentrations in the brain and retina of the eye during the fetal stage and in the period after birth.
Semen also contains it. Electrochemical signals pass through cell membranes faster, perhaps allowing us to think and see better. Research has shown that rhesus monkeys fed low Omega-3 diets produced visually impaired offspring.
An Omega-3 deficiency in laboratory rats disrupts their ability to learn and remember. Research has also shown that premature infants who didn't breastfeed do better physically and mentally when they receive Omega-3s in their diets.
Highly polyunsaturated fatty acids, Omega-3, are found in human milk. Everything that appears in human milk has a purpose. Experts advise infants or pregnant women to eat fish several times a week.
WHAT VARIETY OF FISH SHOULD I EAT?

The best thing is to have a variety of them, saltwater, and freshwater. Trout are excellent, but saltwater fish contain more Omega-3. Their best sources are fatty ones such as salmon and sardines.
If you only have one can of tuna to eat, don't despair. Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology say canned fish retains almost all of its Omega-3s. Canned sardines are also excellent and contain a lot of calcium.
Last year, Americans consumed six kilos of fish, one and a quarter more than seven years ago.
It is one of the leanest proteins we can eat. Even the most greasy ones are less so than the so-called lean meats. What usually makes it unacceptable is the way we prepare it.
Avoid very fried ones along with sauces and creams. Lemon juice is best. In the past, people ate fish because it was cheap - or only on Fridays, for religious reasons. Seafood was unimportant and even dismissed.
FISH OIL SUPPLEMENTS
Are fish oil supplements helpful and healthy? Is it worth spending the money on them? The American Heart Association does not currently recommend them because it is not convinced that they will be useful in the long run.
Not all scientist believe that Omega-3 acts as a heart protector. It could be a different component or a combination of elements that works. Fish oil supplements can liquefy both the blood and lead to bleeding in case of injury or when combined with other drugs such as aspirin.
Fish oil supplements may help certain people who do not eat fish. Medical experts say that too much of that supplement can lead to a deficiency in vitamin E, the controversial antioxidant. Cod liver oil overdoses can overload us with vitamins A and D, which is already toxicity.
Fish oil is fat. Most capsules contain one gram, equivalent to 9 calories. If we take 3 to 6 a day, we will get an excess of 54 calories a day and 2 kilos of fat in a year.
Take it from a variety of sources, but not from fish caught in heavily polluted areas. Now fish is expensive, and you have to look for affordable species.
Less popular species are much cheaper and contain the same proteins and sometimes less fat. Their type of fat is mainly polyunsaturated.
The way we prepare fish will determine the amount of fat we will intake. The more fatty ones, such as salmon, swordfish, trout or tuna, are better cooked or grilled. Lean meats are best steamed or poached.

If you replace a quarter-kilo steak with a fish of identical Omega-3 equivalence, you will have saved calories. Over a year and by eating fish a couple of times a week, you'll lose three kilos or need to exercise less. And your health will also reap many benefits.
