What is the difference between heterozygous and homozygous individuals?

Homozygous and heterozygous are terms that describe different types of allele pairs. People with two identical alleles (RR or rr) are called homozygous. People with different alleles (Rr) are called heterozygous.
The term "homozygous" comes from the Greek "homo," meaning "same," while the word "heterozygous" comes from the Greek "hetereo," meaning "different." The terms describe the relationship between alleles, which are gene variations.
Alleles can be either dominant or recessive. One allele will be expressed in a heterozygous pair while the other is masked. For example, in a heterozygous pair consisting of one R allele and one r allele, the R allele will be expressed, and the r allele will be masked.
In contrast, in a homozygous pair, both alleles are expressed. For example, both alleles will be described in a homozygous pair of two R alleles. The terms homozygous and heterozygous are important in genetics because they help to determine an individual's phenotype.
- What is the definition of heterozygous individuals?
- What is the definition of homozygous individuals?
- Some examples of heterozygous and homozygous traits
- How do you determine if an individual is heterozygous or homozygous?
- What are the benefits of being a heterozygous or homozygous individual?
- The bottom line
What is the definition of heterozygous individuals?
Heterozygous individuals are defined as individuals who have two different alleles for a given trait. In comparison, homozygous individuals are defined as individuals who have two identical alleles for a given feature.
For example, if an individual has the allele for brown eyes (B) and the allele for blue eyes (b), they would be heterozygous for eye color. However, they would be homozygous if they instead had two copies of the allele for brown eyes (BB).
Heterozygosity offers advantages and disadvantages when compared to homozygosity. One advantage is that it can increase genetic diversity, which can be beneficial in maintaining population health.
However, one disadvantage is that it can also lead to higher levels of genetic disorders, as there is a greater chance of expressing recessive alleles.
What is the definition of homozygous individuals?
In genetics, a homozygous individual has two identical alleles for a particular gene. That means that the individual inherited the same allele from each parent.
For example, if both parents have blue eyes, their child will also be homozygous for the blue-eyed allele.
However, if only one parent has blue eyes and the other has brown eyes, the child will be heterozygous for eye color. In other words, they will have one allele for blue eyes and one allele for brown eyes.
Although homozygosity is relatively rare in nature, it can occur when inbreeding or when a mutation occurs.
Some examples of heterozygous and homozygous traits
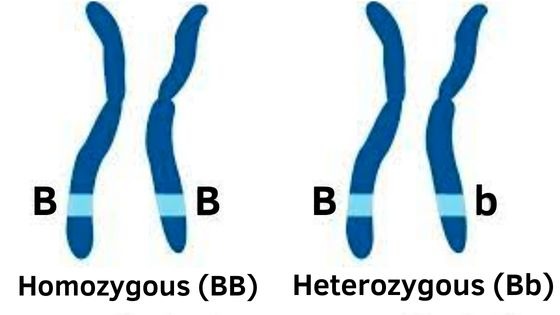
Heterozygous traits are determined by genes that differ, while homozygous characteristics are determined by genes that are the same.
For example, a heterozygous trait might be determined by a gene for blue eyes and a gene for brown eyes, while two genes for blue eyes would determine a homozygous trait. Standard heterozygous features include hair, eye, and skin color.
Homozygous traits are much less common, but they can still be found in specific populations. For example, albinism is a condition caused by a mutation in the gene that determines skin pigmentation.
This mutation is usually passed down from parents to children, resulting in a group of people with very pale skin carriers of the same mutated gene.
While heterozygous and homozygous traits can both be helpful in understanding genetics, it's important to remember that most people are a mix of both types of traits.
How do you determine if an individual is heterozygous or homozygous?
There are two ways to determine if an individual is heterozygous or homozygous.
Looking at their phenotype
The first way is to look at the individual's phenotype or physical appearance. If the individual has one physical trait different from the norm, then they are heterozygous for that trait. For example, if an individual has blue eyes and their parents have brown eyes, they are heterozygous for eye color.
Looking at their genotype
The other way to determine if an individual is heterozygous or homozygous is to look at their genotype or genetic makeup.
If the individual has two alleles for a particular gene, they are heterozygous.
For example, if an individual has the allele for brown eyes and the allele for blue eyes, they are heterozygous for eye color.
If an individual has two identical alleles for a particular gene, they are homozygous.
For example, if an individual has two alleles for brown eyes, they are homozygous for eye color.
In summary, you can determine if an individual is heterozygous or homozygous by looking at their phenotype or genotype.
What are the benefits of being a heterozygous or homozygous individual?
There are many benefits of being heterozygous or homozygous.
- For one, it helps to ensure that an individual has a diverse gene pool. This diversity helps to increase the chances that the individual will be able to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Additionally, heterozygosity also protects against certain diseases. Studies have shown that heterozygous individuals for specific genes are less likely to develop certain conditions, such as cancer.
- Finally, being heterozygous or homozygous can also affect an individual's appearance. For example, individuals who are heterozygous for the gene that causes red hair are more likely to have red hair than individuals who are homozygous for this gene.
In sum, there are many advantages to being heterozygous or homozygous.
The bottom line
Heterozygous and homozygous individuals have different genetic makeups, which give them both advantages and disadvantages.
Have you ever wondered if you were heterozygous or homozygous? Check out our other articles for more information on this fascinating topic.
DISCLAIMER: buildyourbody.org does not provide medical advice, examination, or diagnosis.
Medically reviewed and approved by Nataniel Josue M D.

